AMR MAY, 2021
prepared by Fouzia Nahid
Our May digest features recent research and review articles relating to AMR, screening of ARGs in various environments and metagenomics.
Join the JUNE AMR WEBINARS to discuss the latest AMR insights with us and our invited speakers!
You can register for the next webinars
* on June 9 with Dearbháile Morris and Rabaab Zahra, and
* on June 30 with Kimberly Kline and Sofia Forslund.
On June 25, Big Data Biology Lab is doing an NGLess tutorial for processing metagenomes.
Read more about the tool HERE
Time: Noon UTC
Registration HERE
Global
🇵🇰 Review: Progress on the national action plan of Pakistan on antimicrobial resistance (AMR): a scoping review and the implications – Zikria Saleem – Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy
The social dilemmas of climate change and antibiotic resistance: an analytic comparison and discussion of policy implications – Niklas Harring – Humanities and Social Sciences Communications
*This article analyses climate change and antimicrobial resistance within the context of game theory. Previous literature has identified these problems as common tragedies, where inherent incentive structures encourage selfish overuse of existing resources. While the game theoretical models provide a helpful conceptual basis, the present analysis suggests discrepancies between some of the theoretical assumptions and the practical realities of climate change and antimicrobial resistance.
Review: Antibiotic resistance: time of synthesis in a post-genomic age – Teresa Gil-Gil – Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal
*The authors analyzed the capacities and drawbacks of the tools that are currently in use for the global analysis of AR, aiming to identify the more useful targets for effective corrective interventions.
Diversity of metal and antibiotic resistance genes in Enterococcus spp. from the last century reflects multiple pollution and genetic exchange among phyla from overlapping ecosystems – Andreia Rebelo – Science of The Total Environment
*The authors explored occurrence, diversity, and phenotypes associated with known acquired genes/operons conferring tolerance to As, Hg or Cu among Enterococcus and identified their genetic context.
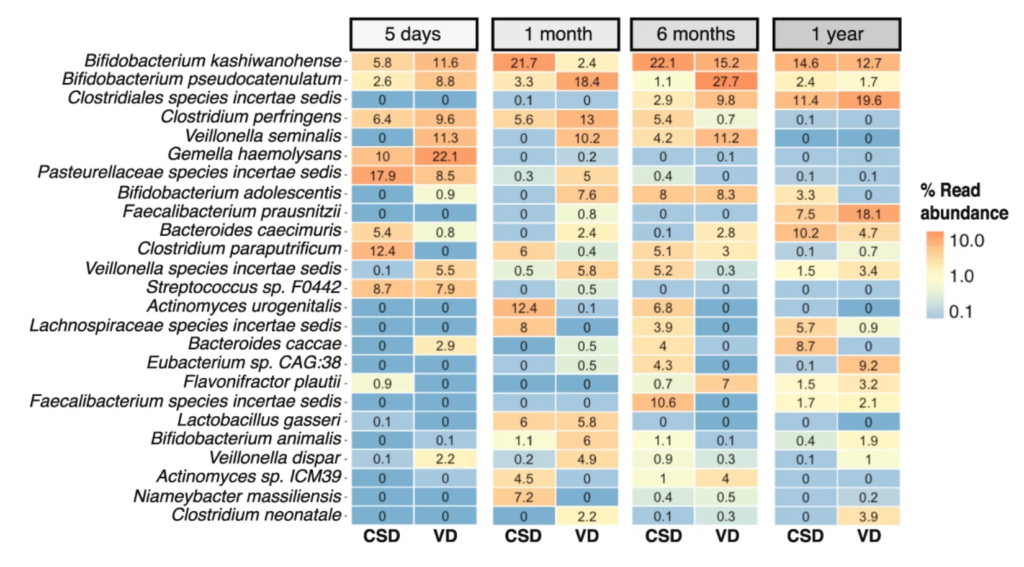
Human-associated microbiome and resistome
Emergence and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli causing bloodstream infections in Norway in 2002–17: a nationwide, longitudinal, microbial population genomic study – Rebecca A Gladstone – THE LANCET Microbe
*The authors aimed to evaluate the clonal diversity underpinning trends in multidrug resistant Escherichia coli causing bloodstream infections which usually remains uncertain. They determined the contribution of individual clones to resistance over time, using large-scale genomics-based molecular epidemiology.
Review: The innate resistome of “recalcitrant” Acinetobacter baumannii and the role of nanoparticles in combating these MDR pathogens – Vasudevan Aparna – Applied Nanoscience
*The authors emphasize the role of intrinsic resistome involved in the antibiotic resistance of A. baumannii, the understanding of which will be very helpful in combating this opportunistic pathogen.
Trade-Offs Between Antibacterial Resistance and Fitness Cost in the Production of Metallo-β-Lactamases by Enteric Bacteria Manifest as Sporadic Emergence of Carbapenem Resistance in a Clinical Setting – Ching Hei Phoebe Cheung – Antimicrobial Agent and Chemotherapy
Reconstruction of ancient microbial genomes from the human gut – Marsha C. Wibowo – Nature
Mobile antimicrobial resistance genes in probiotics – Adrienn Gréta Tóth – bioRxiv
*The authors raised clinical and public health concerns as the consumption of probiotic products may lead to the transfer of ARGs to human gut bacteria.
Review Article: Antimicrobial resistance in nephrology – Tina Z. Wang – Nature Reviews Nephrology
Soil environment
Novel Soil-Derived Beta-Lactam, Chloramphenicol, Fosfomycin and Trimethoprim Resistance Genes Revealed by Functional Metagenomics – Inka Marie Willms – Antibiotics (Basel)
*The authors screened metagenomic libraries comprising of genes of cultivated microorganisms and uncultured microbial for novel ARGs from forest and grassland soils. Three new beta-lactam, a so far unknown chloramphenicol, a novel fosfomycin, as well as three previously undiscovered trimethoprim resistance genes are described in this study.
Manure Microbial Communities and Resistance Profiles Reconfigure after Transition to Manure Pits and Differ from Those in Fertilized Field Soil – Kimberley V. Sukhum – mBio
*The authors evaluated that on dairy farms, the storage of cow manure in manure pits and subsequent application to field soil as a fertilizer may facilitate the spread of the mammalian gut microbiome and its associated ARGs to the environment. To determine the extent of both taxonomic and resistance similarity during these transitions, they collected fresh manure, manure from pits, and field soil across 15 different dairy farms for three consecutive seasons and used a combination of shotgun metagenomic sequencing and functional metagenomics to quantitatively interrogate taxonomic and ARG compositional variation on farms.
Dissipation of antibiotic resistance genes in manure-amended agricultural soil – Liang-Ying He – Science of The Total Environment
*This study provides insight into the dissipation of antibiotic resistance genes in manure-applied agricultural soil. The continuous application of manure results in accumulation of ARGs which persists in soil for at least two years.
Metagenomics analysis reveals the distribution and communication of antibiotic resistance genes within two different red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii cultivation ecosystems – Limin Fan – Environmental Pollution
*This study showed that MacB and BcrA are two dominant ARGs, and macrolide is the dominant antibiotic not only in the water, but also in the sediment and gut of crayfish, in both the crayfish monoculture and the rice-crayfish cultivation ecosystems.
Distribution of the microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes in farmland surrounding gold tailings: A metagenomics approach – Longkai Qiao – Science of The Total Environment
*The authors studied microbes and antibiotic resistance genes in farmland near gold tailings. The main ARGs exhibited macrolide, lincosaminide, and streptogramin B resistance. Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Acidobacteria were the main carriers of ARGs. The microbial community was the most important driver of soil ARG distribution.
Environmental fate of tetracycline antibiotics: degradation pathway mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives – Ahmad Fiaz – Environmental Sciences Europe
*The authors collected data on the available degradation strategies, mechanisms involved in biodegradable and non-biodegradable routes, the main factor affecting degradation strategies, compiled novel detection techniques of tetracycline antibiotics in the environment, and discussed antibiotic resistance genes and their potential role in degradation.
Water environment
Wastewater treatment plants as a reservoir of integrase and antibiotic resistance genes – An epidemiological threat to workers and environment – Wiktor Zieliński – Environmental International
*The authors found a significant increase in the quantities of ARGs and concentrations of antibiotics in the river following the discharge of treated wastewater in comparison to their amounts in the river water upstream from the point of discharge. A higher concentration of ARGs was detected in the DNA from swabs obtained from the wastewater treatment plant employees than from ones collected from the control group.
Built environment
Characterization of the public transit air microbiome and resistome reveals geographical specificity – M. H. Y. Leung – Microbiome
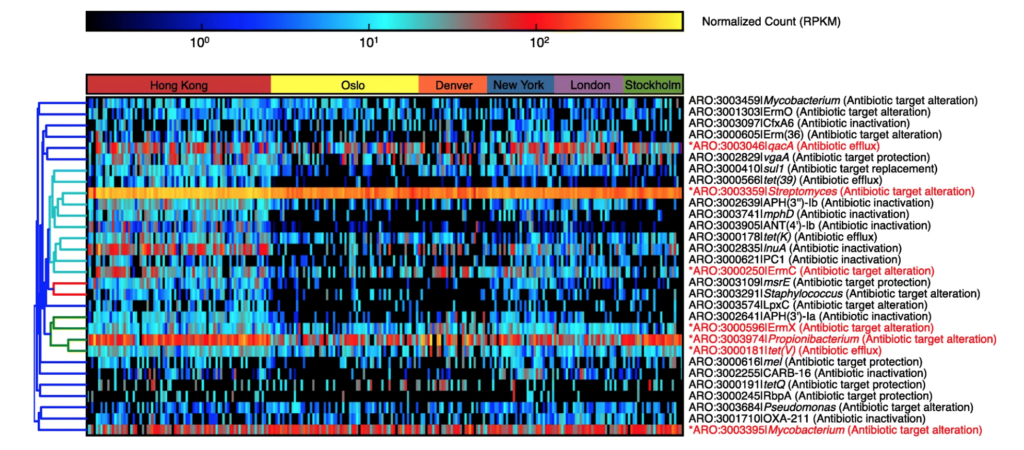
Heatmap of the top 30 AR protein families based on average reads per kilobase per million (RPKM) reads across metagenomes. Core AR protein families (those detected in ≥ 75% of the entire dataset) are indicated in red and asterisks
A global metagenomic map of urban microbiomes and antimicrobial resistance – David Danko – Cell
Phages
Aminoglycoside antibiotics inhibit phage infection by blocking an early step of the phage infection cycle – Larissa Kever – bioRxiv
*The authors have described how aminoglycosides, a well-known class of antibiotics produced by Streptomyces, act as potent inhibitors of phage infection in widely divergent bacterial hosts.
COVID-19
Antibody-dependent enhancement and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and therapies – Wen Shi Lee – Nature Microbiology
*The authors described the key ADE mechanisms and discussed mitigation strategies for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and therapies in development and about the risk of ADE in SARS-CoV-2. They outline recently published data to evaluate the risks and opportunities for antibody-based protection against SARS-CoV-2.
Sample storage
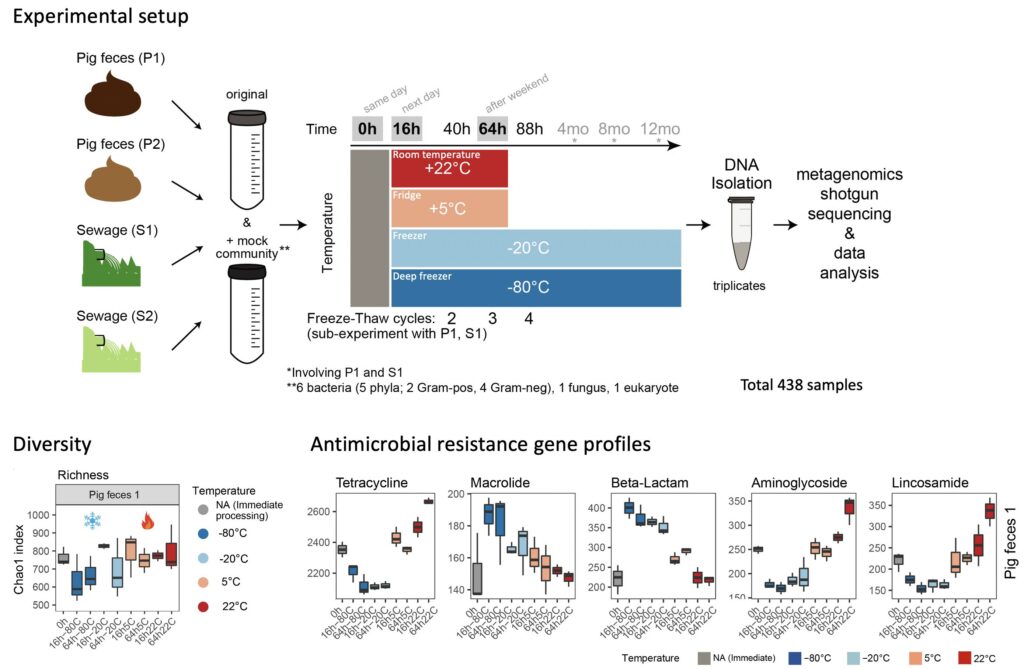
Standard Sample Storage Conditions Impact on Inferred Microbiome Composition and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns – Casper S. Poulsen –bioRxiv
*The authors examined the effect of common sample storage conditions on metagenomics-based microbiome composition and found significant and, in part, systematic effects.
Bioinformatics
A machine learning framework to predict antibiotic resistance traits and yet unknown genes underlying resistance to specific antibiotics in bacterial strains – Janak Sunuwar – Briefing in Bioinformatics
*There are several strains of bacteria lacking known resistance genes; however, they demonstrate resistance phenotype to drugs of that family. In this study, authors present a machine learning framework to predict novel AMR factors that are potentially responsible for resistance to specific antimicrobial drugs which may help proactive interventions.
Podcast
Listen to the AMS case studies illustrating the importance of antimicrobial stewardship and how it works in practice.
Rachel Irwin & the visual culture of AMR. WHO report on the antibacterial pipeline. Neonatal sepsis in LMICs. – The AMR Studio – Uppsala Antibiotic Center